배열 Arrays
배열(array)은 한 가지 타입의 고정된 갯수의 값을 보유하고 있는 container 객체입니다.
배열의 길이(length)는 배열이 생성될 때 정해집니다.
생성되고 나면 배열의 길이는 고정됩니다.
이러한 배열은 애플리케이션 "Hello World!"의 메소드 main 안에서 이미 본 적이 있습니다.
이 섹션에서 배열을 보다 상세하게 논의합니다.
An array is a container object that holds a fixed number of values of a single type. The length of an array is established when the array is created. After creation, its length is fixed. You have seen an example of arrays already, in the main method of the "Hello World!" application. This section discusses arrays in greater detail.
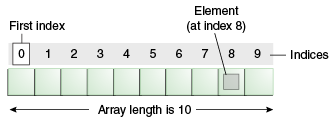
An array of 10 elements.
배열 안의 각 item을 element라고 하며, 숫자 색인(index)으로 각 항목에 접근할 수 있습니다.
앞의 예제에서 보이는 것 처럼, index의 numbering은 0부터 시작합니다.
예를 들어 9번째 항목은 따라서 index 8로 접근할 수 있습니다.
Each item in an array is called an element, and each element is accessed by its numerical index. As shown in the preceding illustration, numbering begins with 0. The 9th element, for example, would therefore be accessed at index 8.
다음 프로그램 ArrayDemo는 정수들의 배열을 만들어서 그 배열 안에 몇 가지 값들을 집어넣은 다음, 표준 output으로 각 값을 인쇄합니다.
The following program, ArrayDemo, creates an array of integers, puts some values in the array, and prints each value to standard output.
class ArrayDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { // 정수들의 배열을 선언합니다 declares an array of integers
int[] anArray; // 10개의 정수에 대하여 메모리를 할당합니다 allocates memory for 10 integers
anArray = new int[10]; // 첫 째 엘리먼트를 초기화합니다 initialize first element
anArray[0] = 100;
// 두 번째 엘리먼트를 초기화합니다 initialize second element
anArray[1] = 200;
// and so forth anArray[2] = 300; anArray[3] = 400; anArray[4] = 500; anArray[5] = 600; anArray[6] = 700; anArray[7] = 800; anArray[8] = 900; anArray[9] = 1000; System.out.println("Element at index 0: " + anArray[0]); System.out.println("Element at index 1: " + anArray[1]); System.out.println("Element at index 2: " + anArray[2]); System.out.println("Element at index 3: " + anArray[3]); System.out.println("Element at index 4: " + anArray[4]); System.out.println("Element at index 5: " + anArray[5]); System.out.println("Element at index 6: " + anArray[6]); System.out.println("Element at index 7: " + anArray[7]); System.out.println("Element at index 8: " + anArray[8]); System.out.println("Element at index 9: " + anArray[9]); } }
The output from this program is:
Element at index 0: 100
Element at index 1: 200
Element at index 2: 300
Element at index 3: 400
Element at index 4: 500
Element at index 5: 600
Element at index 6: 700
Element at index 7: 800
Element at index 8: 900
Element at index 9: 1000
실세계 프로그래밍 상황에서, 앞선 예제에서와 같이 개별적으로 각 라인을 작성하기 보다는, 배열의 각 엘리먼트를 통하여 반복하기 위하여 아마도 지원되는 looping constructs 중 하나를 사용할 것입니다.
하지만, 예제는 명백하게 배열 신택스를 예시하고 있습니다.
Control Flow section에서 다양한 looping constructs (for, while, do-while)를 배울 것입니다.
In a real-world programming situation, you would probably use one of the supported looping constructs to iterate through each element of the array, rather than write each line individually as in the preceding example. However, the example clearly illustrates the array syntax. You will learn about the various looping constructs (for, while, and do-while) in the Control Flow section.
배열을 참조하는 변수 선언하기 Declaring a Variable to Refer to an Array
앞선 프로그램은 다음의 코드 라인을 가진 배열(이름이 anArray인)을 선언합니다:
The preceding program declares an array (named anArray) with the following line of code:
// 정수들의 배열을 선언합니다
int[] anArray;
Like declarations for variables of other types, an array declaration has two components: the array's type and the array's name. An array's type is written as type[], where type is the data type of the contained elements; the brackets are special symbols indicating that this variable holds an array. The size of the array is not part of its type (which is why the brackets are empty). An array's name can be anything you want, provided that it follows the rules and conventions as previously discussed in the naming section. As with variables of other types, the declaration does not actually create an array; it simply tells the compiler that this variable will hold an array of the specified type.
Similarly, you can declare arrays of other types:
byte[] anArrayOfBytes; short[] anArrayOfShorts; long[] anArrayOfLongs; float[] anArrayOfFloats; double[] anArrayOfDoubles; boolean[] anArrayOfBooleans; char[] anArrayOfChars; String[] anArrayOfStrings;
You can also place the brackets after the array's name:
// this form is discouraged float anArrayOfFloats[];
However, convention discourages this form; the brackets identify the array type and should appear with the type designation.
배열만들기, 초기화하기, 접근하기
Creating, Initializing, and Accessing an Array
One way to create an array is with the new operator. The next statement in the ArrayDemo program allocates an array with enough memory for 10 integer elements and assigns the array to the anArray variable.
// create an array of integers anArray = new int[10];
If this statement is missing, then the compiler prints an error like the following, and compilation fails:
ArrayDemo.java:4: Variable anArray may not have been initialized.
The next few lines assign values to each element of the array:
anArray[0] = 100; // initialize first element anArray[1] = 200; // initialize second element anArray[2] = 300; // and so forth
Each array element is accessed by its numerical index:
System.out.println("Element 1 at index 0: " + anArray[0]);
System.out.println("Element 2 at index 1: " + anArray[1]);
System.out.println("Element 3 at index 2: " + anArray[2]);
Alternatively, you can use the shortcut syntax to create and initialize an array:
int[] anArray = {
100, 200, 300,
400, 500, 600,
700, 800, 900, 1000
};
Here the length of the array is determined by the number of values provided between braces and separated by commas.
You can also declare an array of arrays (also known as a multidimensional array) by using two or more sets of brackets, such as String[][] names. Each element, therefore, must be accessed by a corresponding number of index values.
In the Java programming language, a multidimensional array is an array whose components are themselves arrays. This is unlike arrays in C or Fortran. A consequence of this is that the rows are allowed to vary in length, as shown in the following MultiDimArrayDemo program:
class MultiDimArrayDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[][] names = {
{"Mr. ", "Mrs. ", "Ms. "},
{"Smith", "Jones"}
};
// Mr. Smith
System.out.println(names[0][0] + names[1][0]);
// Ms. Jones
System.out.println(names[0][2] + names[1][1]);
}
}
The output from this program is:
Mr. Smith Ms. Jones
Finally, you can use the built-in length property to determine the size of any array. The following code prints the array's size to standard output:
System.out.println(anArray.length);
배열 복사하기 Copying Arrays
The System class has an arraycopy method that you can use to efficiently copy data from one array into another:
public static void arraycopy(Object src, int srcPos,
Object dest, int destPos, int length)
The two Object arguments specify the array to copy from and the array to copy to. The three int arguments specify the starting position in the source array, the starting position in the destination array, and the number of array elements to copy.
The following program, ArrayCopyDemo, declares an array of char elements, spelling the word "decaffeinated." It uses the System.arraycopy method to copy a subsequence of array components into a second array:
class ArrayCopyDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
char[] copyFrom = { 'd', 'e', 'c', 'a', 'f', 'f', 'e',
'i', 'n', 'a', 't', 'e', 'd' };
char[] copyTo = new char[7];
System.arraycopy(copyFrom, 2, copyTo, 0, 7);
System.out.println(new String(copyTo));
}
}
The output from this program is:
caffein
배열 조작 Array Manipulations
Arrays are a powerful and useful concept used in programming. Java SE provides methods to perform some of the most common manipulations related to arrays. For instance, the ArrayCopyDemo example uses the arraycopy method of theSystem class instead of manually iterating through the elements of the source array and placing each one into the destination array. This is performed behind the scenes, enabling the developer to use just one line of code to call the method.
For your convenience, Java SE provides several methods for performing array manipulations (common tasks, such as copying, sorting and searching arrays) in the java.util.Arrays class. For instance, the previous example can be modified to use the copyOfRange method of the java.util.Arrays class, as you can see in the ArrayCopyOfDemo example. The difference is that using the copyOfRange method does not require you to create the destination array before calling the method, because the destination array is returned by the method:
class ArrayCopyOfDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
char[] copyFrom = {'d', 'e', 'c', 'a', 'f', 'f', 'e',
'i', 'n', 'a', 't', 'e', 'd'};
char[] copyTo = java.util.Arrays.copyOfRange(copyFrom, 2, 9);
System.out.println(new String(copyTo));
}
}
As you can see, the output from this program is the same (caffein), although it requires fewer lines of code. Note that the second parameter of the copyOfRange method is the initial index of the range to be copied, inclusively, while the third parameter is the final index of the range to be copied, exclusively. In this example, the range to be copied does not include the array element at index 9 (which contains the character a).
Some other useful operations provided by methods in the java.util.Arrays class, are:
- Searching an array for a specific value to get the index at which it is placed (the
binarySearchmethod). - Comparing two arrays to determine if they are equal or not (the
equalsmethod). - Filling an array to place a specific value at each index (the
fillmethod). - Sorting an array into ascending order. This can be done either sequentially, using the
sortmethod, or concurrently, using theparallelSortmethod introduced in Java SE 8. Parallel sorting of large arrays on multiprocessor systems is faster than sequential array sorting.
'Java 배우기' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Operators 연산자 (0) | 2016.01.05 |
|---|---|
| Summary of Variables 변수 요약 (0) | 2016.01.05 |
| Primitive Data Types 원시 데이터 타입 (0) | 2016.01.05 |
| Variables 변수 (0) | 2016.01.05 |
| Lesson: Language Basics 단원: 언어 기초 (0) | 2016.01.05 |
댓글