숫자로 작업할 때, 대부분의 경우 코드에서 원시타입을 사용합니다. 예를 들면:
When working with numbers, most of the time you use the primitive types in your code. For example:
int i = 500;
float gpa = 3.65f;
byte mask = 0xff;
하지만 원시 타입 대신 객체를 사용하는 이유가 있으며, 자바 플랫폼은 각각의 원시데이터타입에 대하여 클래스 wrapper를 제공합니다.
이들 클래스 wrapper는 객체 안에서 원시타입을 "wrap" 합니다.
컴파일러가 wrapping을 수행하는 경우도 많습니다 - 객체가 예상되는 곳에 원시타입이 사용된다면, 컴파일러는 그 wrapper 클래스 안에 원시타입을 box 시킵니다.
비슷한 경우로, 원시타입이 예상되는 곳에 숫자 객체가 사용된다면, 컴파일러는 객체를 언박스시킵니다.
보다 많은 정보는 Autoboxing and Unboxing를 참조하십시오.
There are, however, reasons to use objects in place of primitives, and the Java platform provides wrapper classes for each of the primitive data types. These classes "wrap" the primitive in an object. Often, the wrapping is done by the compiler—if you use a primitive where an object is expected, the compiler boxes the primitive in its wrapper class for you. Similarly, if you use a number object when a primitive is expected, the compiler unboxes the object for you. For more information, see Autoboxing and Unboxing
모든 숫자 wrapper 클래스들은 추상 클래스 Number의 하위클래스 입니다.
All of the numeric wrapper classes are subclasses of the abstract class Number:
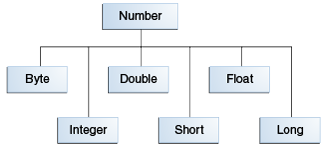
Note: There are four other subclasses of
Number that are not discussed here. BigDecimal and BigInteger are used for high-precision calculations. AtomicInteger and AtomicLong are used for multi-threaded applications.There are three reasons that you might use a Number object rather than a primitive:
- As an argument of a method that expects an object (often used when manipulating collections of numbers).
- To use constants defined by the class, such as
MIN_VALUEandMAX_VALUE, that provide the upper and lower bounds of the data type. - To use class methods for converting values to and from other primitive types, for converting to and from strings, and for converting between number systems (decimal, octal, hexadecimal, binary).
The following table lists the instance methods that all the subclasses of the Number class implement.
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
byte byteValue() | Converts the value of this Number object to the primitive data type returned. |
int compareTo(Byte anotherByte) | Compares this Number object to the argument. |
boolean equals(Object obj) | Determines whether this number object is equal to the argument. The methods return true if the argument is not null and is an object of the same type and with the same numeric value.There are some extra requirements for Double and Float objects that are described in the Java API documentation. |
Each Number class contains other methods that are useful for converting numbers to and from strings and for converting between number systems. The following table lists these methods in the Integer class. Methods for the other Numbersubclasses are similar:
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
static Integer decode(String s) | Decodes a string into an integer. Can accept string representations of decimal, octal, or hexadecimal numbers as input. |
static int parseInt(String s) | Returns an integer (decimal only). |
static int parseInt(String s, int radix) | Returns an integer, given a string representation of decimal, binary, octal, or hexadecimal (radix equals 10, 2, 8, or 16 respectively) numbers as input. |
String toString() | Returns a String object representing the value of this Integer. |
static String toString(int i) | Returns a String object representing the specified integer. |
static Integer valueOf(int i) | Returns an Integer object holding the value of the specified primitive. |
static Integer valueOf(String s) | Returns an Integer object holding the value of the specified string representation. |
static Integer valueOf(String s, int radix) | Returns an Integer object holding the integer value of the specified string representation, parsed with the value of radix. For example, if s = "333" and radix = 8, the method returns the base-ten integer equivalent of the octal number 333. |
'Java 배우기' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Beyond Basic Arithmetic 기본 산술을 넘어서 (0) | 2016.01.05 |
|---|---|
| Formatting Numeric Print Output (0) | 2016.01.05 |
| Numbers 숫자 (0) | 2016.01.05 |
| Lesson: Numbers and Strings 단원: 숫자와 문자 (0) | 2016.01.05 |
| Questions and Exercises: Inheritance 질문과 연습: 상속 (0) | 2016.01.05 |
댓글