Cardiovascular 심혈관
연구에 따르면 NMN은 쥐의 혈관노화를 막습니다
Study Shows NMN Stops Blood Vessel Aging in Mice
NAD+ 감소는 쥐에서 심혈관 질환을 유발하는 데 도움이 되며, 이는 전구체 NMN으로 완화될 수 있습니다
NAD+ decline helps drive cardiovascular disease in mice, which can be mitigated with the precursor NMN
By Jonathan D. Grinstein, Ph.D.
Published: 12:17 p.m. PST Jun 22, 2021 | Updated: 12:04 p.m. PST Sep 29, 2021
Highlights
· #NAD+ 를 소비하는 효소인 CD38 결핍은 고혈압 및 #심혈관질환 관련 혈관변화를 완화합니다.
Deficiency of CD38 — an enzyme that consumes NAD+ — alleviates high blood pressure and cardiovascular disease-related blood vessel changes.
· #NMN 보충 또는 CD38 억제는 혈관 세포주기 정지(노화)를 개선하여 심혈관기능을 회복합니다.
NMN supplementation or CD38 inhibition restores cardiovascular function by ameliorating blood vessel cell cycle arrest (senescence).
CD38은 400개 이상의 중요한 세포활동의 보조인자인 #니코틴아미드 아데닌 디뉴클레오티드(NAD+)의 분해를 위한 주요 효소이며, 이 과정은 노화에 기여하는 것으로 나타났습니다.
CD38 is the main enzyme for the degradation of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) — a cofactor in 400+ critical cellular activities — a process shown to contribute to aging.
신호변환 및 표적치료(Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy)에 발표된 글에서 쓰촨대학과 난창대학 연구원들은 CD38과 관련 세포내 NAD+ 감소가 죽상경화증 및 고혈압 등 연령 관련 심혈관질환을 유발하는 과정에 중요하다는 것을 보여줍니다.
In their article published in Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy, researchers from Sichuan University and Nanchang University show that CD38 and the associated intracellular NAD+ decline are critical for processes that drive age-related cardiovascular diseases, such as atherosclerosis and hypertension.
CD38이 없거나, CD38 억제제나 NAD+ 전구체 니코틴아미드 모노뉴클레오타이드(NMN)가 보충된 쥐에서, 연구자들은 고혈압을 제한하고 세포가 더 이상 복제할 수 없는 영구적 상태인 #혈관세포 노화를 증가시켜 심혈관질환 발병을 차단했습니다.
In mice lacking CD38 or supplemented with a CD38 inhibitor or the NAD+ precursor nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN), the researchers blocked the development of cardiovascular diseases by limiting high blood pressure and increases in blood vessel cell senescence — a permanent state when cells can no longer replicate.
또한, 연구자들은 CD38 결핍 또는 NAD+ 보충이 손상되지 않은 인접 #세포노화 를 촉진하는 #세포외소포 라는 세포간 신호 payloads를 억제함으로써 혈관세포 노화를 현저하게 완화시키는 것을 관찰했습니다.
In addition, the researchers observed that CD38 deficiency or NAD+ supplementation remarkably mitigated senescence of blood vessel cells by suppressing signaling payloads between cells called extracellular vesicles that facilitated the senescence of neighboring non-damaged cells.
연구원들은 “NAD-boosting” 요법과 CD38 억제제 적용은 노화관련 질병을 치료하기 위한 새로운 전략이 될 수 있다고 제안했습니다“
"NAD-boosting’ therapy and the application of CD38 inhibitors may be novel strategies for treating age-related diseases,” proposed the researchers.
노화는 심혈관질환을 유발할 수 있습니다
Senescence can drive cardiovascular disease
심혈관질환의 발병률은 나이가 들수록 크게 증가합니다.
The incidence of cardiovascular diseases significantly increases with aging.
노화되는 세포축적(영구적 세포주기 정지상태)은 노화의 특징이며 #심부전 , #죽상동맥경화증 및 고혈압 등 심혈관질환의 병리학적 진행에 관여하는 것으로 입증되었습니다.
The accumulation of cells that become senescent — a state of permanent cell cycle arrest — is a hallmark of aging and has been demonstrated to be involved in the pathological progression of cardiovascular diseases, including heart failure, atherosclerotic disorder, and hypertension.
혈관 평활근 세포(VSMC) 노화는 병적 혈관 리모델링 및 고혈압 조절의 악화에 기여합니다.
The senescence of vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) contributes to pathological vascular remodeling and the deterioration of hypertension control.
NAD+ decline drives senescence of blood vessel cells
NAD+ 감소는 혈관세포 노화를 유도합니다
이 연구는 CD38을 유전적으로 제거하거나 억제제로 CD38을 차단하는 것이 #심혈관질환 발병 모델인 쥐에서 화학적으로 유도된 혈관 리모델링을 유의하게 완화한다는 것을 보여주었습니다.
This study showed that genetically removing CD38 or blocking CD38 with an inhibitor significantly alleviated chemically-induced vascular remodeling in mice, a model for cardiovascular disease development.
연구자들이 쥐에서 CD38을 유전적으로 삭제했을 때, 이 동물들은 고혈압(고혈압), 혈관벽 두께 증가(혈관이 더 뻣뻣하고 기능이 떨어지는 것을 나타냄), 혈관 무결성을 유지하는 데 중요한 단백질 수준와 같은 심혈관질환을 유발하는 과정이 개선되었습니다.
When the researchers genetically deleted CD38 from mice, these animals had improvements in processes that drive cardiovascular diseases, such as high blood pressure (hypertension), increased thickness of the blood vessel wall (indicative of stiffer and less functional blood vessels) , and alterations in the level of proteins critical for maintaining blood vessel integrity.
그들의 결과는 또한 CD38 결핍이 화학적으로 유도된 DNA 손상을 유의하게 약화시키고 이들 쥐의 동맥에 있는 VSMC에서 노화 관련 마커의 축적을 감소시킨다는 것을 보여주었습니다.
Their results also showed that CD38 deficiency significantly attenuated chemically-induced DNA damage and reduced the accumulation of senescence-associated markers in VSMCs in the arteries of these mice.
"현재 연구에서 우리는 CD38이 고혈압에서 #혈관리모델링 에 기여했을 뿐만 아니라 VSMC 노화에서 해로운 #노화촉진 역할을 한다는 것을 입증하여 NAD 감소와 노화의 상관관계를 추가로 확인했습니다"라고 연구원들은 결론지었습니다.
“In the current study, we demonstrated that CD38 not only contributed to vascular remodeling in hypertension but also played a detrimental pro-senescence role in VSMC senescence, further confirming the correlation of NAD decline and aging,” concluded the researchers.
Boosting NAD+ levels alleviates hypertension and vascular remodeling
NAD+ 수치를 높이면 고혈압과 혈관 리모델링이 완화
연구원들은 또한 NAD+ 보충제가 VSMC 노화를 구제할 수 있는지 여부를 조사했습니다.
The researchers also examined whether NAD+ supplementation can rescue VSMC senescence.
건강한 조건에서, 전체 대동맥 조직의 세포내 NAD+ 수준은 수정되지 않은 쥐에 비해 CD38이 결핍된 쥐에서 거의 50% 증가했습니다. Under healthy conditions, the intracellular NAD+ levels of whole aorta tissue were increased by nearly 50% in mice lacking CD38 compared with unmodified mice.
또한 NAD+ 수치를 높이기 위해 NMN(300 mg/kg)을 경구 투여하면 화학적으로 유발된 고혈압이 완화되었습니다.
Moreover, oral administration of NMN (300 mg/kg) to elevate NAD+ levels alleviated chemically-induced hypertension.
이 고혈압 쥐에서 NMN(i.p., 10 mg/kg/dose)을 주사한 후 혈관 매체 두께, 매체 대 루멘 비율 및 콜라겐 침착이 각각 26%, 27% 및 30% 감소했습니다.
In these hypertensive mice, the vascular media thickness, media-to-lumen ratio, and collagen deposition were reduced by 26%, 27%, and 30%, respectively, following injection with NMN (i.p., 10 mg/kg/dose).

(Gan et al., 2021 | Signal Transduct Target Ther.) NMN alleviated hypertension and vascular remodeling in mice. (a) Caudal artery blood pressures were detected in mice with or without NMN administration every 7 days after infusion with a hypertension-inducing chemical called angiotensin II (Ang II). (b) The carotid artery’s systolic and diastolic blood pressures were detected in mice with or without NMN administration 4 weeks after Ang II infusion.
세포배양에서, 연구자들은 VSMC에 외인성 NAD+(100μM)를 사전 투여하고 Ang II 유도 #세포노화 지표를 감지했습니다.
In cell culture, the researchers pre-administered exogenous NAD+ (100 μM) to VSMCs and detected Ang II-induced cell senescence indicators.
그 결과 노화세포 양성 부위가 54% 감소한 것으로 나타났습니다.
The results showed that the area positive for senescent cells was decreased by 54%.
또한 연구자들이 CD38의 수준을 높이면 VSMC의 노화수준이 크게 증가했습니다.
In addition, when the researchers increased the levels of CD38, the levels of senescence of VSMCs significantly increased.
이러한 결과는 CD38이 #항노화 치료를 위한 잠재적인 약리학적 표적이 될 수 있음을 강력하게 뒷받침합니다.
These results strongly supported that CD38 may be a potential pharmacological target for anti-senescence treatment.
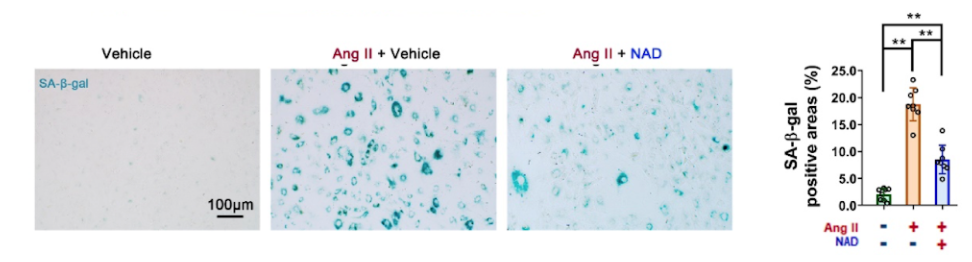
(Gan et al., 2021 | Signal Transduct Target Ther.) NAD+ supplementation restored Ang II-induced cell senescence in vascular smooth muscle cells. NAD+ (100 μM) was added into the medium of vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) for 4 hours before Ang II administration. All these compounds were maintained in the medium for 3 days. And then the VSMCs were stained by a marker for senescence (SA-β-gal).
CD38 및 NAD+는 노화를 유도하는 세포간 운반물 컨테이너를 제어
CD38 and NAD+ control intercellular cargo containers that induce senescence
연구자들은 CD38 결핍이 세포를 둘러싸고 있는 동일한 지방으로 만들어진 구형 용기인 세포외 소포의 생성, 분비 및 내재화를 억제함으로써 VSMC 노화를 감소시킨다는 것을 입증했습니다.
The researchers demonstrated that CD38 deficiency reduced VSMC senescence by suppressing the genesis, secretion, and internalization of extracellular vesicles — spherical containers made of the same fat that encases cells.
이러한 구조는 노화과정에서 인접 세포노화를 촉진하는 분자를 포함하여 세포와 기관 사이에 분자를 전달할 수 있습니다.
These structures can deliver molecules between cells and organs, including molecules that promote neighboring cell senescence in aging processes.
이 연구에서 Ang II-챌린지된 평활근 세포에서 유래한 작은 세포외 소포는 손상되지 않은 인접 세포의 노화를 가속화했습니다.
In this study, small extracellular vesicles derived from Ang II-challenged smooth muscle cells accelerated the senescence of neighboring undamaged cells.
더욱이, 이러한 작은 세포외 소포는 노화세포에 의해 쉽게 내재화되어 이들 세포 노화과정을 악화시켰습니다.
Moreover, these small extracellular vesicles were easily internalized by senescent cells, exacerbating the aging process in these cells.
NMN 건강전문 몰
www.dopza.com

“따라서 이러한 결과는 고혈압에서 VSMC 노화 기전에 대한 우리의 이해를 높이고 혈관노화를 줄이기 위한 새로운 치료 목표에 대한 통찰력을 제공한다고 저자들은 결론지었습니다.
"우리의 결과는 CD38 억제 또는 NAD 보충이 노화관련 질병에 대한 잠재적 치료 전략 역할을 할 수 있다는 강력한 증거를 제공합니다."
"Accordingly, these results advance our comprehension of the mechanisms of VSMC senescence in hypertension and provide insight into novel therapeutic targets for reducing vascular aging,” concluded the authors.
“Our results provide strong evidence that CD38 inhibition or NAD supplementation may serve as potential therapeutic strategies for age-related diseases.”
|
Blood Pressure
|
|
Cardiovascular Disease
|
|
Hypertension
|
|
NAD+
|
|
Senescence
|
Story Source
Gan L, Liu D, Liu J, Chen E, Chen C, Liu L, Hu H, Guan X, Ma W, Zhang Y, He Y, Liu B, Tang S, Jiang W, Xue J, Xin H. CD38 deficiency alleviates Ang II-induced vascular remodeling by inhibiting small extracellular vesicle-mediated vascular smooth muscle cell senescence in mice. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021 Jun 11;6(1):223. doi: 10.1038/s41392-021-00625-0. PMID: 34112762.
812
'NMN' 카테고리의 다른 글
| NMN 암치료 화학요법 인지장애 예방 (0) | 2022.02.02 |
|---|---|
| NMN 노화방지 효과 (0) | 2022.02.02 |
| NMN 뇌졸중 (0) | 2022.02.02 |
| NAD+ 강화, 뇌허혈 후 미토콘드리아 건강 향상 (0) | 2022.02.02 |
| NMN의 과학 - 안정적이고 신뢰할 수 있는 NAD+활성화제 및 노화방지 분자 (0) | 2022.01.22 |




댓글