Neurological 신경과
연구에 따르면 NMN은 설치류의 뇌졸중을 지연시킵니다.
Study Shows NMN Delays Stroke in Rodents
혈압이 증가하고 뇌졸중 소인이 있는 쥐는 NAD+ 수치가 감소했습니다
Rats with increased blood pressure and stroke predisposition have decreased NAD+ levels
By Jonathan D. Grinstein, Ph.D.
Published: 11:38 am PST Mar 22, 2021 | Updated: 12:22 p.m. PST Sep 29, 2021
Highlights
· 결함이 있는 세포 재활용 과정은 고염식을 먹인 쥐에서 고혈압과 관련된 자발적 뇌졸중을 유발합니다.
· Defective cell recycling processes favor hypertension-related spontaneous stroke in rats fed high-salt diets.
· NMN 치료는 이러한 설치류의 뇌졸중 발생을 방지하기 위해 이러한 과정을 역전시킵니다.
· NMN treatment reverses these processes to protect against stroke occurrence in these rodents.
뇌졸중은 사망 및 장애의 주요 원인이며 유전적 구성과 혈압을 높이는 생활방식 등 다양한 위험요소를 가지고 있습니다.
Stroke is a leading cause of mortality and disability and has an array of risk factors including our genetic makeup and lifestyles that increase blood pressure, or what’s called hypertension in the medical field.
현재까지 이 질병에 대한 효과적 치료법이 없으므로 고혈압이 #뇌졸중 에 걸리기 쉬운 방법을 파악하면 예방 및 치료 전략을 개선할 수 있습니다.
To date, there are no effective treatments for this disease, so figuring out how hypertension predisposes people to stroke may improve its preventive and therapeutic strategies.
#고혈압 관련 뇌졸중의 발병에서 #자가포식 ( #autophagy )으로 알려진 세포의 재활용 과정의 역할에 대한 힌트가 있었지만 이 연관성은 여전히 불분명합니다.
Although there have been hints for the role of the cell’s recycling processes known as autophagy in the development of hypertension-related stroke, this connection remains unclear.
로마 사피엔자대학의 Forte와 동료들은 Autophagy 저널에 결함이 있는 자가포식이 에너지 생성을 담당하는 세포구조인 미토콘드리아의 기능 장애를 촉진하여 고혈압 관련 자발적 뇌졸중에 유리하다는 글을 발표했습니다.
Forte and colleagues from the Sapienza University of Rome published an article in the journal Autophagy showing that defective autophagy favors hypertension-related spontaneous stroke by promoting dysfunction of the mitochondria, the cell structures responsible for generating energy.
이탈리아 연구팀은 쥐에게 고혈압을 유발하고 뇌졸중 위험을 증가시키기 위해 고염식을 먹인 결과 설치류 뇌에서 자가포식이 감소하는 것을 발견했습니다.
The Italian research team fed rats high-salt diets to cause hypertension and increase the risk of stroke and found a reduction of autophagy in the rodent brains.
자가포식의 이러한 손상은 미토콘드리아 기능장애 및 필수 생체 에너지 분자인 #니코틴아미드 아데닌 디뉴클레오티드(NAD)+의 고갈과 관련이 있습니다.
This impairment in autophagy was linked to mitochondrial dysfunction and depletion of the essential bioenergetic molecule nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD)+.
연구자들이 니코틴아미드 #모노뉴클레오타이드 (NMN)로 NAD+ 수준을 회복시켰을 때, 그들은 뇌졸중에 걸리기 쉬운 쥐에서 자가포식의 재활성화와 뇌졸중 발병 감소를 보았습니다.
When the researchers restored NAD+ levels with nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN), they saw a reactivation of autophagy and reduced stroke development in the stroke-prone rats.
이러한 발견은 NAD+ 수준을 높이고 자가포식을 활성화하기 위한 중재가 뇌졸중 발병 위험이 더 높은 대상에 대한 새로운 치료 전략을 나타낼 수 있음을 시사합니다.
These findings suggest that interventions aimed to boost NAD+ levels and activate autophagy may represent novel therapeutic strategies for subjects at higher risk to develop stroke.
Autophagy가 뇌졸중의 핵심입니까?
Is Autophagy at the Heart of Stroke?
단세포 유기체에서 가장 복잡한 다세포 유기체에 이르기까지 자가포식은 손상된 세포 구성요소를 제거하는 데 중요한 역할을 합니다.
From single-cell organisms to the most complex multicellular ones, autophagy plays a vital role in the removal of damaged cellular components.
#미토파지 라는 자가포식의 한 유형은 손상된 미토콘드리아의 제거에 전념하여 미토콘드리아 품질관리를 보장합니다.
One type of autophagy called #mitophagy is devoted to the clearance of damaged mitochondria, ensuring mitochondrial quality control.
Autophagy는 일반적으로 스트레스에 대한 반응으로 활성화되어 기능 장애 미토콘드리아를 제거한 다음 새로 형성된 건강한 미토콘드리아로 대체됩니다.
Autophagy is usually activated in response to stress to remove dysfunctional mitochondria, which are then substituted with newly formed healthy ones.
자가포식의 손상은 적절한 미토콘드리아 회전율의 부족으로 이어지며 결과적으로 미토콘드리아 기능장애가 발생하여 뇌졸중을 비롯한 #심혈관질환 진행으로 이어질 수 있습니다.
Impairment of autophagy leads to the lack of a proper mitochondrial turnover with the resulting development of mitochondrial dysfunction, which can lead to the progression of cardiovascular diseases, including stroke.
미토콘드리아 기능장애는 혈류부족으로 인한 뇌 손상의 주요 결정요인인 에너지고갈, 유해한 산소 함유 분자 축적(산화스트레스) 및 염증을 유발합니다.
Mitochondrial dysfunction causes energy depletion, harmful oxygen-containing molecule buildup (oxidative stress), and inflammation, which are all major determinants of brain injury due to lack of blood flow.
이러한 라인을 따라 autophagy 억제는 미토콘드리아 기능장애를 촉진하고 위험요소가 있는 경우 뇌졸중에 대한 감수성을 증가시킵니다.
Along these lines, autophagy inhibition would favor mitochondrial dysfunction and increase the susceptibility to stroke in the presence of risk factors.
그러나 뇌졸중 발병에서 autophagy의 정확한 역할은 아직 해결되지 않았습니다.
But the exact role of autophagy in the development of stroke remains unsolved.
NMN은 자가포식 결함을 역전시키고 뇌졸중 발생으로부터 보호합니다
NMN Reverses Autophagy Defects and Protects Against Stroke Occurrence
Forte와 동료들은 인간 뇌졸중 연구에 적합한 모델을 나타내는 뇌졸중 경향이 있는 고혈압 쥐에서 자가포식 장애와 자발적 뇌졸중 발병 사이의 연관성을 테스트했습니다.
Forte and colleagues tested the link between autophagy impairment and spontaneous stroke development in stroke-prone hypertensive rats, which represents a suitable model for the study of human stroke.
이 쥐 모델은 7주 동안 고나트륨 및 저칼륨 식이를 하면 발병률이 100%인 자발적인 뇌졸중이 발생합니다.
This rat model develops spontaneous stroke, with an incidence of 100% after 7 weeks of high sodium and low potassium diet.
이 모델에서 뇌졸중 발생은 미토콘드리아 기능장애, 산화스트레스, 뇌와 뇌 혈관계의 염증의 발달이 선행되어 결국 뇌 부종과 뇌졸중으로 이어집니다.
In this model, the occurrence of stroke is preceded by the development of mitochondrial dysfunction, oxidative stress, and inflammation in brains and cerebral vasculature, which finally leads to brain edema and stroke.
이탈리아 연구팀은 고염식 식이 섭취에 대한 반응으로 뇌졸중이 발생하기 쉬운 쥐의 자가포식 억제가 뇌의 세포내 NAD+ 수치의 급격한 하락에 의존한다는 것을 발견했습니다.
The Italian research team found that autophagy inhibition in these stroke-prone rats in response to high salt dietary feeding is dependent on the dramatic drop of intracellular NAD+ levels in the brain.
그러나 이 설치류에 NAD+ 전구체 NMN(250mg/kg)을 매일 주사했을 때 Forte와 동료들은 뇌에서 NAD+ 수준을 구했고, 이는 자가포식, 손상된 미토콘드리아 제거 및 미토콘드리아 기능의 개선과 관련이 있었습니다.
But when they injected these rodents with the NAD+ precursor NMN (250 mg/kg) daily, Forte and colleagues rescued NAD+ levels in the brain, which was linked to improvements in autophagy, the clearance of damaged mitochondria, and mitochondrial function.
그들은 또한 고염식으로 뇌졸중에 걸리기 쉬운 쥐의 뇌에서 혈관세포의 생존이 증가하는 것을 보았습니다.
They also saw an increase in the survival of blood vessel cells in the brains of rats predisposed to stroke with high salt diets.

(Forte et al. 2020 | Autophagy)
NMN은 배양된 세포에서 미토콘드리아 기능과 세포 생존력을 개선했습니다. 마우스 혈관세포에 염(NaCl) 또는 자가포식억제제(siRNA)를 처리한 후 미토콘드리아 손상 정도(좌)와 생존율(우)을 평가하였다. 염 및 자가포식 억제제 치료는 모두 미토콘드리아 손상을 증가시키고 살아있는 세포의 비율을 감소시켰습니다. 그러나 두 경우 모두에서 이러한 효과는 NMN을 보충함으로써 역전되었습니다. NMN improved mitochondrial function and cell viability in cultured cells. Mouse blood vessel cells were treated with salt (NaCl) or an inhibitor of autophagy (siRNA) and then evaluated for the degree of mitochondrial damage (left) and viability (right). Both the salt and autophagy inhibitor treatments caused increases in mitochondrial damage and decreases in the percentage of live cells. These effects in both cases, however, were reversed by supplementation with NMN.
중요하게도, NMN은 염분 섭취가 많은 뇌졸중이 발생하기 쉬운 쥐에서 뇌졸중 발생을 크게 둔화시켰습니다.
Importantly, NMN strongly blunted stroke occurrence in high salt-fed stroke-prone rats.
특히, NMN을 투여받은 동물의 절반 이상이 고염식이를 공급한 처리되지 않은 쥐와 비교하여 뇌졸중에서 12주까지 생존했습니다.
Notably, more than half of the animals receiving NMN survived from stroke until the 12th week as compared to the untreated rats fed with a high salt diet.
Forte와 동료들은 자가포식을 활성화하여 고염식 식이를 먹인 쥐의 뇌졸중 소인의 뿌리에 기능장애 자가포식이 있음을 2배로 보여주었습니다.
Forte and colleagues then doubled down on showing that dysfunctional autophagy was at the root of stroke predisposition in the high salt diet fed rats by activating autophagy.
특히, 뇌졸중 예방에 있어 자가포식을 자극하는 보호효과는 혈압 수준과 무관하게 발생했습니다.
Notably, the protective effect of stimulating autophagy in preventing stroke occurred independent of blood pressure levels.
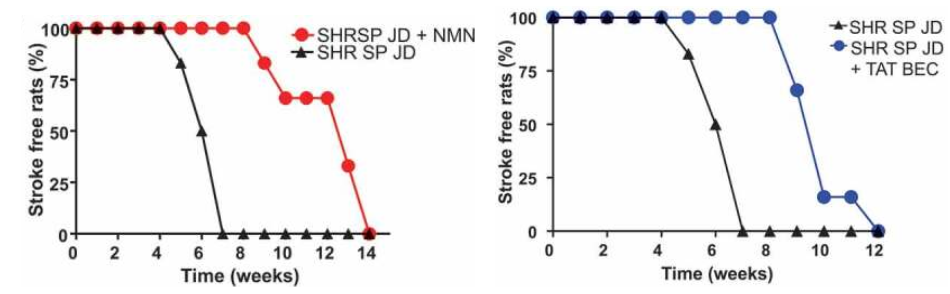
(Forte et al. 2020 | Autophagy) NMN으로 자가포식을 자극하면 고염식을 먹인 쥐에서 뇌졸중 없는 생존이 증가했습니다. 플롯은 고염식(JD)을 먹인 뇌졸중이 발생하기 쉬운 고혈압 쥐(SHRSP)에서 뇌졸중 발생을 보여줍니다. 그런 다음 이 마우스를 NMN(+NMN) 또는 자가포식 자극제(+TAT BEC)로 처리했습니다. 두 경우 모두 뇌졸중의 유병률이 거의 2배 지연되었습니다 Stimulating autophagy with NMN increased stroke-free survival in rats fed high salt diets. The plots show the stroke occurrence in stroke-prone hypertensive rats (SHRSP) fed high salt diets (JD). These mice were then treated with either NMN (+NMN) or a stimulator of autophagy (+TAT BEC). In both cases, the prevalence of stroke was delayed nearly two-fold.
이러한 결과는 autophagy 손상이 #뇌혈관손상 및 뇌졸중 발생의 발병에 기여할 수 있음을 분명히 나타냅니다.
These results clearly indicate that autophagy impairment may contribute to the development of cerebrovascular damage and stroke occurrence.
자가포식 재활성화는 기능장애 미토콘드리아 제거에 유리하고 고염 치료에 대한 반응으로 내피 및 대뇌 세포 손상을 제한하여 뇌 손상의 발병을 지연시킬 수 있습니다.
Autophagy reactivation may favor the removal of dysfunctional mitochondria and limit the damage of endothelial and cerebral cells in response to high salt treatment, thereby delaying the onset of brain injury.
결론적으로, 이러한 발견은 자가포식을 활성화하고 NAD+ 수준을 높이는 것을 목표로 하는 중재가 뇌졸중 발병 위험이 더 높은 피험자를 위한 새로운 치료전략을 나타낼 수 있음을 시사합니다.
In conclusion, these findings suggest that interventions aimed to activate autophagy and boost NAD+ levels may represent novel therapeutic strategies for subjects at higher risk to develop stroke.
NMN 건강전문 몰
www.dopza.com

흡수율 최고 리포조말 비타민C 글루타치온 콜라겐 CBD Hemp 오일 전문
www.dopza.com
Story Source
Forte M, Bianchi F, Cotugno M, Marchitti S, De Falco E, Raffa S, Stanzione R, Di Nonno F, Chimenti I, Palmerio S, Pagano F, Petrozza V, Micaloni A, Madonna M, Relucenti M, Torrisi MR, Frati G, Volpe M, Rubattu S, Sciarretta S. Pharmacological restoration of autophagy reduces hypertension-related stroke occurrence. Autophagy. 2020 Aug;16(8):1468-1481. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2019.1687215. Epub 2019 Nov 12. PMID: 31679456; PMCID: PMC7469607.
1,310
'NMN' 카테고리의 다른 글
| NMN 암치료 화학요법 인지장애 예방 (0) | 2022.02.02 |
|---|---|
| NMN 노화방지 효과 (0) | 2022.02.02 |
| NMN은 혈관노화를 막습니다 (0) | 2022.02.02 |
| NAD+ 강화, 뇌허혈 후 미토콘드리아 건강 향상 (0) | 2022.02.02 |
| NMN의 과학 - 안정적이고 신뢰할 수 있는 NAD+활성화제 및 노화방지 분자 (0) | 2022.01.22 |




댓글